INTRODUCTION
-
Nucleic acids are energy molecules that derive
metabolic processes in all cells.
-
These nucleic acids form our DNA, which is
referred as our heredity material.
NUCLEOTIDE
-
It is the actual molecule that makes up our DNA
(deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid) as well.
-
DNA is our genetic material whereas RNA makes
up our genetic code.
-
DNA is more likely to be found in nucleus and
less in cytoplasm.
-
RNA is more likely to be found in cytoplasm and
less in nucleus.
-
Upon hydrolysis of DNA three components are
obtained: -
o
Phosphoric acid
o
Pentose sugar
o
Nitrogenous base
NITROGENOUS BASES
-
These are most important constituent of both DNA
and RNA.
-
These are classified into two groups based upon
their structure: -
o
Purines
o
Pyrimidines
-
PYRIMIDINES
o
It is heterocyclic (a cyclic compound with more
than one type of atoms) compound.
o
Pyrimidines constitute of three nitrogenous
bases
o
Thymine: -
§
Found only in DNA.
§
Chemical composition C5H6O2N2.
o
Cytosine: -
§
Found both in DNA and RNA.
§
Chemical composition is C4H5ON3.
o
Uracil: -
§
Found only in RNA.
§
Chemical composition is C4H4O2N2.
-
PURINES
o
It is a pyrimidine ring that is attached to
another 5-membered ring.
o
Purines constitute of two nitrogenous bases.
o
Adenine: -
§
Found both in DNA and RNA.
§
Chemical composition is C5H5N5.
o
Guanine: -
§
Found both in DNA and RNA.
§
Chemical composition is C5H5ON5.
Pentose sugar
-
It is present in both nucleic acids in two
different forms.
-
The two nucleic acids are distinguished
primarily on the basis of 5-carbon keto sugar or called ribose.
-
DNA has 2-deoxyribose nucleic acid and RNA has ribonucleic acid.
-
Ribose reacts with orcinol in HCl solution
containing FeCl whereas deoxyribose diphenylamine in acidic solution.
-
Compounds containing only nitrogenous bases and
pentose sugars are called nucleosides.
-
Nucleotides contain pentose sugar, nitrogenous
base and phosphate group.
Nucleotides
-
These have several functions in the cell
-
Carriers of chemical energy: -
o
Nucleotides with one, two or three phosphate
groups are called monophosphate, diphosphate or triphosphate.
o
NTPs (nucleotide triphosphate) are sources of
energy in any biochemical reaction.
o
ATP is widely used but other NTPs are used in
specific reactions.
o
Hydrolysis of NTPs releases energy.
-
Enzyme cofactors: -
o
Many enzyme cofactors and coenzymes contain
adenosine as part of their structure.
o
Removal of adenosine from the cofactors
decreases their activity.
o
Example: - acetyl Co-A.
-
Chemical messenger: -
o
Hormones and chemical signalling agents are
called messengers.
o
These messengers induce secondary messengers
inside the cells which are generally nucleotides.
DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid)
-
It is polymer of nucleotide monomers joined by
phosphodiester bonds.
-
Purines and Pyrimidines carry genetic
information whereas pentose sugar and phosphate group perform structural role.
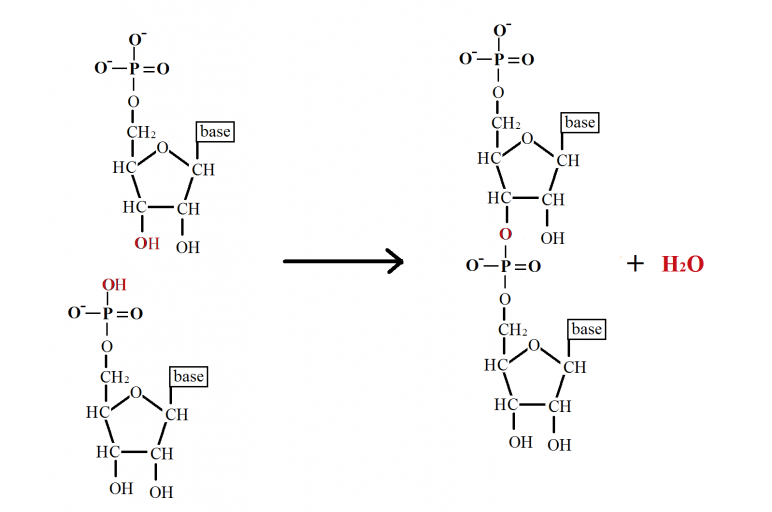
-
In a DNA phosphodiester bond is formed between
5’phosphate group of one nucleotide and 3’hydroxyl group of another nucleotide.
-
This contains four nitrogenous bases adenine,
guanine, thymine and cytosine.
-
RNA is similar but it has Uracil in the place of
thymine.
Structure of DNA by Watson and Crick model
-
The 3D model of DNA was given by James.D.watson
and Fransis.H.crick in 1953.
-
They said that the DNA is double stranded.
-
The two strands were antiparallel one ran from
5’ to 3’ direction and the other ran from 3’ to 5’ direction.
-
Adenine formed double bonded hydrogen bond with
thymine and guanine formed triple bonded hydrogen bond with cytosine.
-
The two strands of a DNA can be represented as a
step ladder folded along its imaginary axis to form a “Double Helix”.
Types of DNA
-
A-DNA
o
Right handed orientation.
o
Found in conditions with low humidity
-
B-DNA
o
Right handed orientation
o
Most dominant form in almost all organisms.
-
Z-DNA
o
Left handed orientation.
o
Its sugar
backbones are zigzag in appearance.
No comments :
Post a Comment